Connect With Us
Skin Biopsy
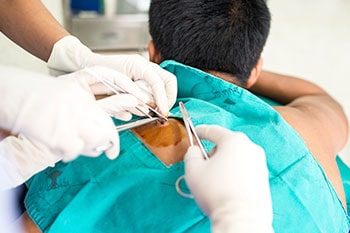
A skin biopsy is a critical diagnostic procedure performed to evaluate and diagnose a variety of skin conditions, ranging from infections and inflammatory diseases to cancerous lesions. This procedure involves the removal of a small sample of skin tissue, which is then examined under a microscope by a dermatopathologist to identify abnormalities and determine the precise nature of the skin condition.
There are several types of skin biopsies, each tailored to specific types of lesions or suspected conditions. A shave biopsy involves slicing off the upper layers of skin, typically used for superficial lesions. A punch biopsy, which uses a circular tool, is suitable for investigating deeper layers of skin, providing a more comprehensive tissue sample. An excisional biopsy, where an entire lump or area of skin is removed, is often performed when a malignant condition is suspected.
The procedure is usually quick, performed under local anesthesia, and can be done in a doctor's office or a clinic. While generally safe, skin biopsies can cause slight discomfort, bleeding, and, in some cases, scarring, depending on the size and depth of the biopsy.
Post-procedure, the biopsy site requires care to prevent infection and ensure proper healing. The results from a skin biopsy can greatly influence the course of treatment, offering guidance on whether further surgical intervention, medication, or other treatments are necessary.
Understanding the outcomes of a skin biopsy can provide patients with crucial information about their skin health, enabling them to make informed decisions about their treatment options. It is a foundational tool in dermatology that aids in the accurate diagnosis and management of numerous skin diseases, contributing to more targeted and effective treatment plans.
